Idea2Data: Toward a New Paradigm for Drug Discovery.
Nicolaou, C.A., Humblet, C., Hu, H., Martin, E.M., Dorsey, F.C., Castle, T.M., Burton, K.I., Hu, H., Hendle, J., Hickey, M.J., Duerksen, J., Wang, J., Erickson, J.A.(2019) ACS Med Chem Lett 10: 278-286
- PubMed: 30891127
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.8b00488
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
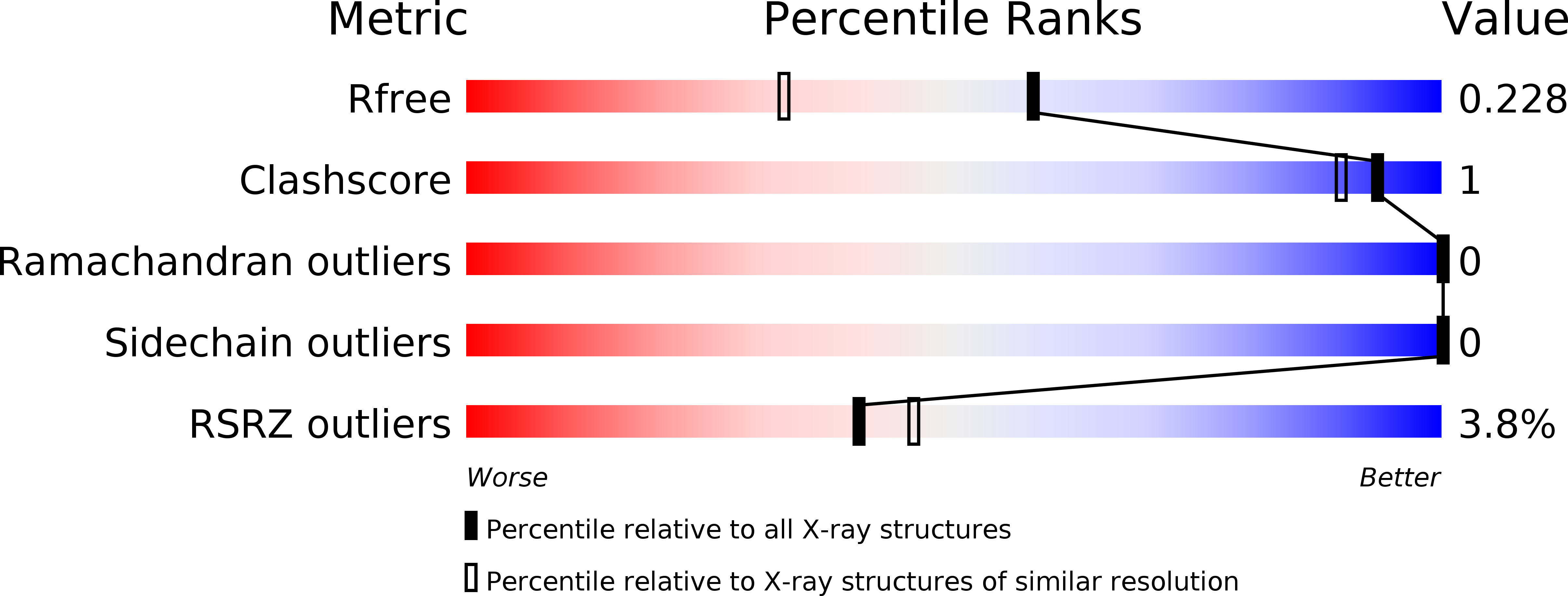
6MNH - PubMed Abstract:
Increasing the success rate and throughput of drug discovery will require efficiency improvements throughout the process that is currently used in the pharmaceutical community, including the crucial step of identifying hit compounds to act as drivers for subsequent optimization. Hit identification can be carried out through large compound collection screening and often involves the generation and testing of many hypotheses based on available knowledge. In practice, hypothesis generation can involve the selection of promising chemical structures from compound collections using predictive models built from previous screening/assay results. Available physical collections, typically used during hit identification, are of the order of 10 6 compounds but represent only a small fraction of the small molecule drug-like chemical space. In an effort to survey a larger portion of chemical space and eliminate inefficiencies during hit identification, we introduce a new process, termed Idea2Data (I2D) that tightly integrates computational and experimental components of the drug discovery process. I2D provides the ability to connect a vast virtual collection of compounds readily synthesizable on automated synthesis systems with computational predictive models for the identification of promising structures. This new paradigm enables researchers to process billions of virtual molecules and select structures that can be prepared on automated systems and made available for biological testing, allowing for timely hypothesis testing and follow-up. Since its introduction, I2D has positively impacted several portfolio efforts through identification of new chemical scaffolds and functionalization of existing scaffolds. In this Innovations paper, we describe the I2D process and present an application for the discovery of new ULK inhibitors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Lilly Research Laboratories, Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana 46285, United States.